Peritonitis Definition Medical Terms
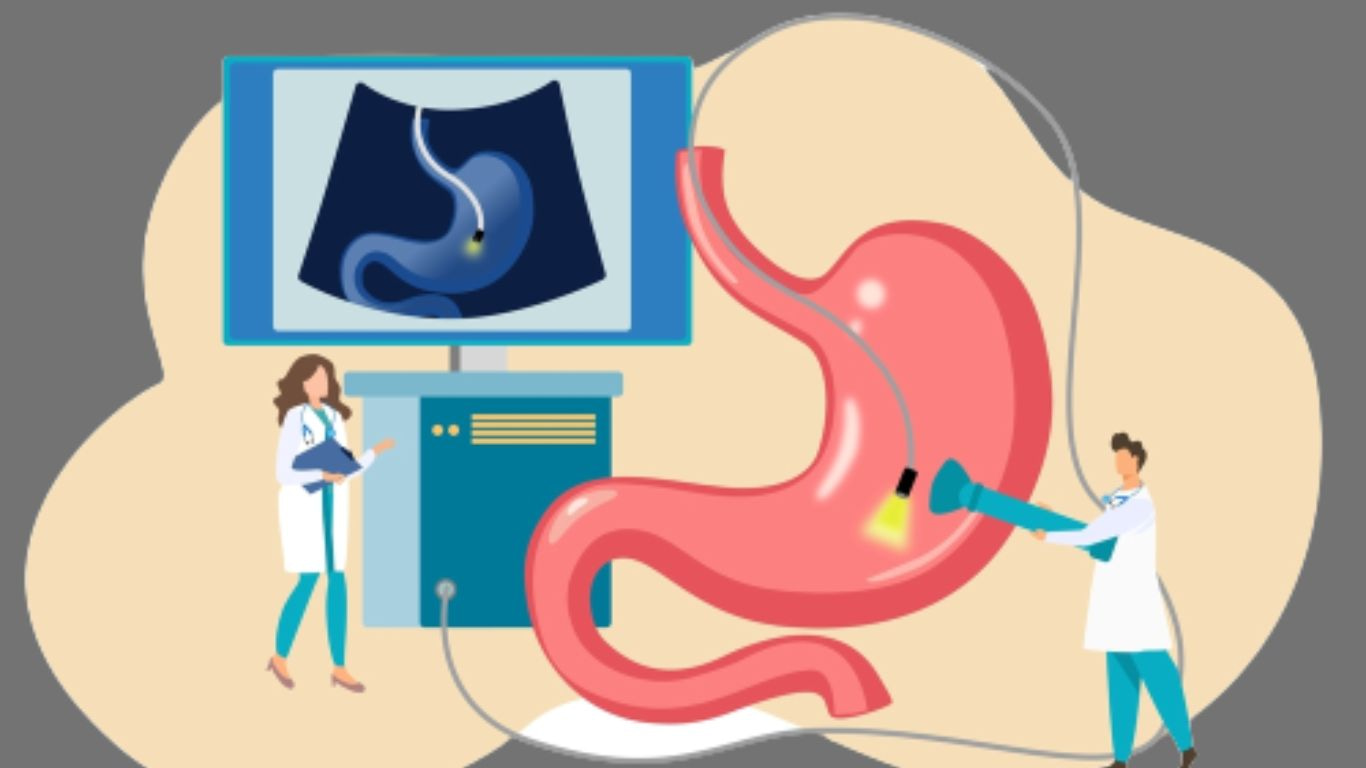
Inflammation of the aqueous membrane of the stomach is called peritonitis.
This disease can be acute or chronic. In a healthy state, a fluid substance called
serous phyllodes is released from this membrane. This fluid keeps the membrane
lubricated, but when it is inflamed, it is released in large quantities, and as the
disease progresses, it turns into acid. Generally, it is observed that this tissue is not
completely inflamed, but the part of it that is above the renal tubule and intestine is
inflamed.
What is the Most Common Cause of Peritonitis?
- C is a bacterial infection.
- This membrane becomes inflamed due to intestinal inflammation.
- Due to stomach ulcers.
- When the blood turns yellow
- Due to injury.
- Sometimes due to another infection.
Peritonitis Symptoms
- Nausea and vomiting occur.
- Stomach
- Have you passed?
- Constipation stops stool completely. Breathing becomes faster.
- Fever occurs.
- A reduction in inflammation occurs at a specific location.
- It also starts coming into the muscles of the body.
- The number of white blood cells increases.
Peritonitis Blood Test Results
- Blood C.B.C tests show an increased white cell count.
- When ESR is performed, the level is high.
Note:
It should be noted that the above-mentioned report applies wherever there
is inflammation in the body.
Peritonitis Treatment in Homeopathic Medicine
-
Aconite 30
This medicine should be given early in the initial illness. There is severe
inflammation, a high fever, panic, restlessness, pain to touch, pain to touch,
etc. Are there symptoms?
-
Belladonna 30
As soon as possible, administer this medicine along with Aconite 30. Very useful.
Ferm Phos 12x Black Peacock 6x Mag Phos 6x
Dissolve this mixture in warm water and sip it every half an hour. As a result,
the disease is controlled quickly in the initial stages, but all of these medicines
are made in Germany.
-
Brai Onya 30
Its symptoms include high fever, increased thirst, increased movement,
constipation, and throbbing pain. This disease does not intensify with
repeated exposure.
-
Merck Year 30
In edema, the stomach is strained to fill the fluid. All the symptoms of the disease
are more intense at night. The patient asked for cold water. Fever causes chills and
frequent sweating, but it does not cause fever or any other symptoms; it only
increases pain. This is a special symptom of this medicine. This medicine works
well after Pella Donna.
Chicken egg yolk peritonitis
The presence of yellow materials in the coelomic cavity can cause an inflammatory
response in the peritoneum, known as egg yolk peritonitis. It is possible for egg yolks
to cause inflammation within the peritoneum even when consumed alone. When bacteria
thrive in the yolk, they cause secondary bacterial infections and organ inflammation,
which can result in morbidity and mortality in flocks, as well as decreased egg production.
There is evidence that egg yolk peritonitis is a contagious disease that is becoming
more common as poultry production expands. The poultry industry will have to deal
with this problem as the incidence and severity of this condition have increased in
recent years. In this area, there is no scientific research on how spontaneous egg yolk
peritonitis affects commercial laying hens and the laying hen industry.
To identify the bacterial agents and pathological alterations in laying hens with
yolk peritonitis, the current study was conducted.
Peritoneal dialysis electrolyte complications
A total of five peritoneal dialysis patients were reported to have hypovolemia, hypernatremia,
alkalisis, and hyperglycemia. An investigation was conducted to determine the nature and
application of commercially available dialysis therapies, as well as the potential causes of
these therapies. Hypertonic solutions can cause hypernatremia and alkalosis when they
contain high sodium and lactate content, especially when fast fluid loss and weight loss
are associated with them. Although rarely required, 7% dextrose solutions are more likely
to cause complications. Excessive fluid loss is possible with 1.5% dextrose solutions,
particularly in patients receiving repeated peritoneal dialysis. Under specific conditions,
a 0.5% dextrose solution containing 34.5 mg/liter of lactate and 135 mEq/liter of salt
may be appropriate.
Dialysis solutions should be selected according to factors such as blood osmolality,
sodium and bicarbonate concentrations, fluid balance status, and glucose tolerance.
Solutions with varying tonicities and electrolyte compositions should be chosen and
evaluated regularly throughout the dialysis process, with adjustments made as necessary.
Most issues can be avoided if potential complications are anticipated and addressed appropriately.
Peritonitis in humans
It is important to remember that the symptoms of peritonitis may vary depending on the
type you have, but they usually include bloating and stomach pain. If you experience
these symptoms, you should be cautious since infections in the peritoneum can damage
multiple organs in your abdomen. In addition to covering a large area of your abdomen,
the peritoneum can affect multiple organs. Moreover, the infection may spread through
your bloodstream throughout your body.
Conclusion
Instruct the patient to rest completely. Warm to the point of pain if the patient
tolerates it. Keep a water bottle handy. Mix the belladonna with the Runkar Glycerin and
massage gently. Suck ice in cases of extreme thirst and give a very light diet.