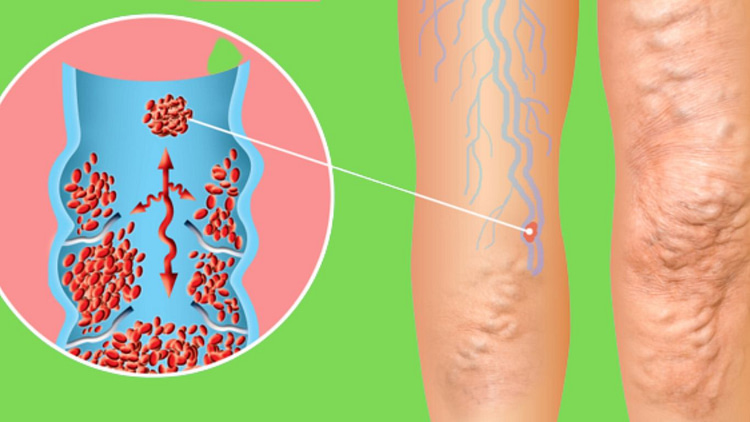
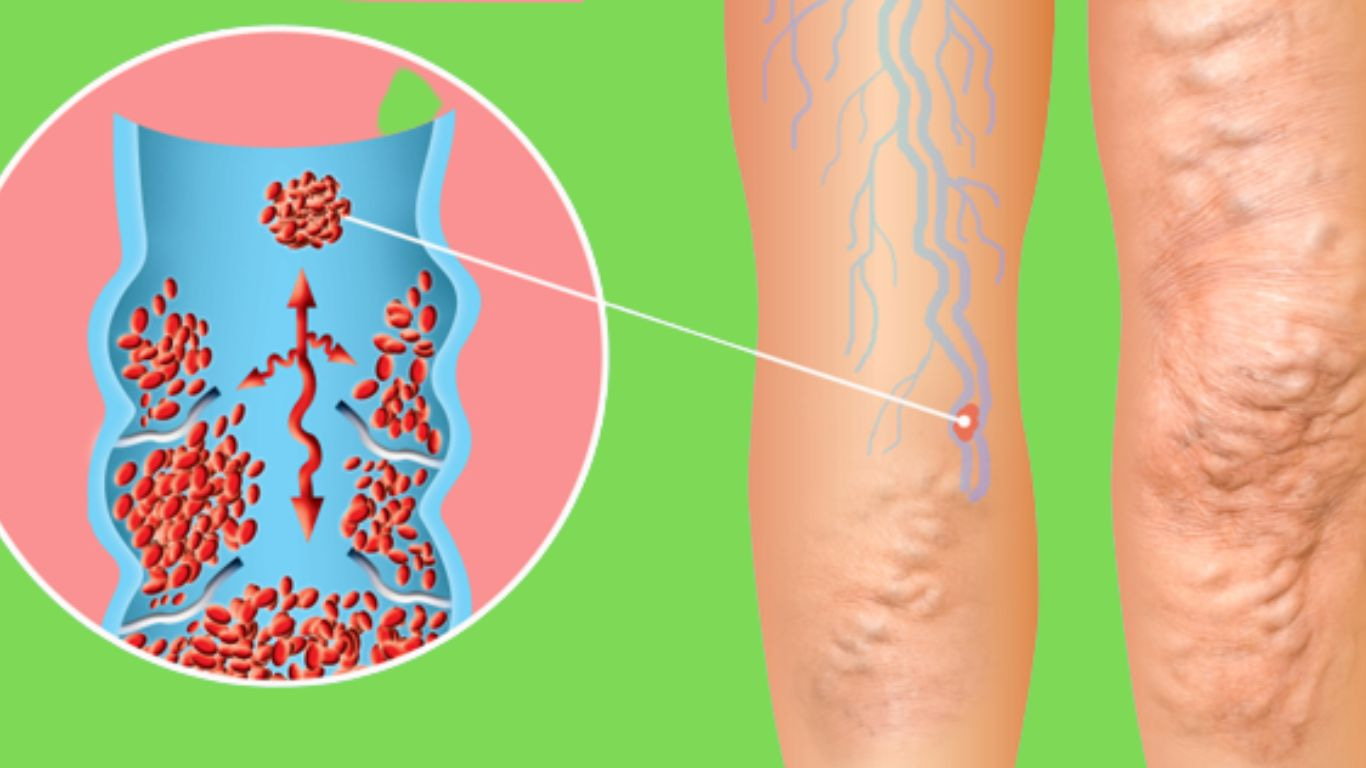
Thrombosis Definition in Pathology
If the blood begins to clot during circulation, it is called a thrombus and
the clot is called a thrombus.
Venous Thrombosis at Unusual Sites
- In the veins of the legs
- In the AORTA.
- It acts as a clot in the brain’s arteries.
- The heart’s arteries contain this substance.
- In the arteries of various organs.
What Causes Thrombosis
- Due to an injury.
- Due to blood changes.
- This disease is common among arthritis patients. As a result of narrowing blood vessels.
- Due to salt in blood flow.
- Due to an operation.
- Changes in blood vessel structure.
- Due to atheroma.
- Atheroma is caused by an excess of cholesterol in the blood vessels (called atheroma).
What are the Symptoms of Thrombosis?
- Swelling
- Pain
- Rapid pulses.
- Thrombosis becomes an abscess.
- Blood in the patient’s saliva.
- The ambit often causes fever.
- High blood pressure.
- Gangrene can also occur due to a thrombus.
- A thrombus causes vascular inflammation.
Thrombosis Treatment in Homeopathic
-
Arnica 6
In this disease, this medicine has proven very effective.
The patient is active, has cold feet, and prefers solitude. Scared at night.
-
Scale Car 630
Numbness in hands and feet and chills. Pain in the heart. High blood pressure
Would have
-
Black Peacock x 6
It is the best medicine to be given every hour of the day.
-
Lyco Podium 6
Its symptoms include rapid heartbeat, albumin excretion in the urine, tightness in the
chest, and difficulty breathing.
-
Fluoric acid 30
This medicine can be beneficial for people who suffer from motion sickness due
to prolonged standing.
-
Plasatilla 630
It is useful for two-layer embossing. Give along with Hema Miles
-
Bothrops 30
In this case, we have the dual answer to Thar Ambush. To be used with other
medicines Should.
Conclusion of Thrombosis
- The patient should be advised to rest completely.
- It is imperative that food is easily digestible in order to prevent constipation.
- Calcium and Vitamin A
- Reduce the consumption of foods containing it.
- Avoid starchy foods.
- Give fibrous food and fruits.
- Control cholesterol.
What is a Thrombosis Test
The same tests are done for this disease as for cholesterol.
Partial portal vein thrombosis
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) refers to the blockage or narrowing of the portal vein
by a blood clot. This condition is not very common and is often linked to prothrombotic
diseases or underlying liver disease. The case study describes a young man who
had been experiencing vague abdominal symptoms for almost a week before being
diagnosed with PVT. In addition to the left portal vein and superior mesenteric vein
being blocked, several non-obstructive blood clots were detected in the right portal vein,
the splenic vein, and the left renal vein on imaging.
We will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for both acute
and chronic thrombosis. It is imperative to thoroughly investigate DVT due to the possibility
that it may indicate underlying conditions such as prothrombotic diseases, liver disease,
and other conditions both systemic and local.
In this case report, we hope to raise awareness among medical professionals
about the difficulties associated with portal vein thrombosis.
Malignant portal vein thrombosis
Malignant DVT cannot be treated with thrombolysis or anticoagulation as the portal vein
is obstructed by live tumor tissue. Patients who are in Child-Pugh Class A and have an
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 to 1, with no
extrahepatic metastases, may receive systemic medication to lower their stage for
locoregional treatment.
Multikinase inhibitors like sorafenib are part of systemic therapy and have been licensed
as a first-line treatment for advanced HCC. Sorafenib has been linked to better overall
survival (OS) compared to a placebo, but its predominant side effects are diarrhea,
tiredness, and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia. Lenvatinib has the same adverse
effects as sorafenib, including hypertension, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and
palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, and has shown a median progression-free survival
of 13.6 versus 12.3 months (HR: 0.92; 95% CI, 0.79-1.06).
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor
and blocks angiogenesis and tumor growth. It selectively targets PD-L1, inhibiting
interactions with PD-1 and B7-1 receptors and antagonizing T cell suppression.
Patients with poorly tolerated locally advanced or metastatic hepatocellular cancer (HCC)
who have not received prior systemic therapy have been cleared for treatment with
bevacizumab by the FDA.
The IMbrave 150 study is a global, multi-center, randomized phase III trial comparing
azo-bev with Saracenic for the treatment of patients with unresectable HCC who have
not previously undergone systemic therapy. The combination of azo-bev demonstrated
a significant improvement in both overall survival (HR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.42-0.79) and
progression-free survival (HR 0.59; 95% CI: 0.47-0.76), showing encouraging results.
Portal vein thrombosis with cavernous transformation
This case study discusses a 58-year-old man who developed a cavernous transformation
of the portal vein (CTPV) due to portal vein thrombosis (PVT). The patient had a history of
persistent alcohol and tobacco use and experienced weakness, general malaise, nausea,
vomiting, anorexia, and weight loss for 25 days. He was admitted to the hospital to rule
out end-stage liver disease or hepatic cancer and to evaluate his abnormal liver function
tests and electrolyte abnormalities. An anaemia assessment did not reveal any cholecystitis,
liver cirrhosis, or hepatic abnormalities, except for a mass holding the stomach and small
intestines in place. Further testing revealed that the liver tumour was PVCT, a rare and fatal
consequence of PVT. In the case of liver tumours, PVCT may be one of the possible
differential diagnoses.







عندما يتعلق الأمر بأنابيب uPVC ، فإن مصنع إيليت بايب Elite Pipe يضع معايير عالية من خلال منتجاته المصممة بدقة والتي توفر حلول سباكة وري موثوقة وخالية من التسرب.